Unequal heating of the Earths surface also forms large global wind patterns. Still flowing in a circular pattern the current flows south as far as the northwestern coast of Africa where it is known as the Canary Currentthe gyres eastern boundary current.
The water at the ocean surface is moved primarily by winds that blow in certain patterns because of the Earths spin and the Coriolis Effect.

. The ball moves in a circular path just like a freely moving particle of gas or liquid moves on the. Air moves in large circular patterns called convection cells. The warm air rises because it is light.
Winds are able to move the top 400 meters of the ocean creating surface ocean currents. Surface ocean currents form large circular patterns called gyres. The air cools until it descends.
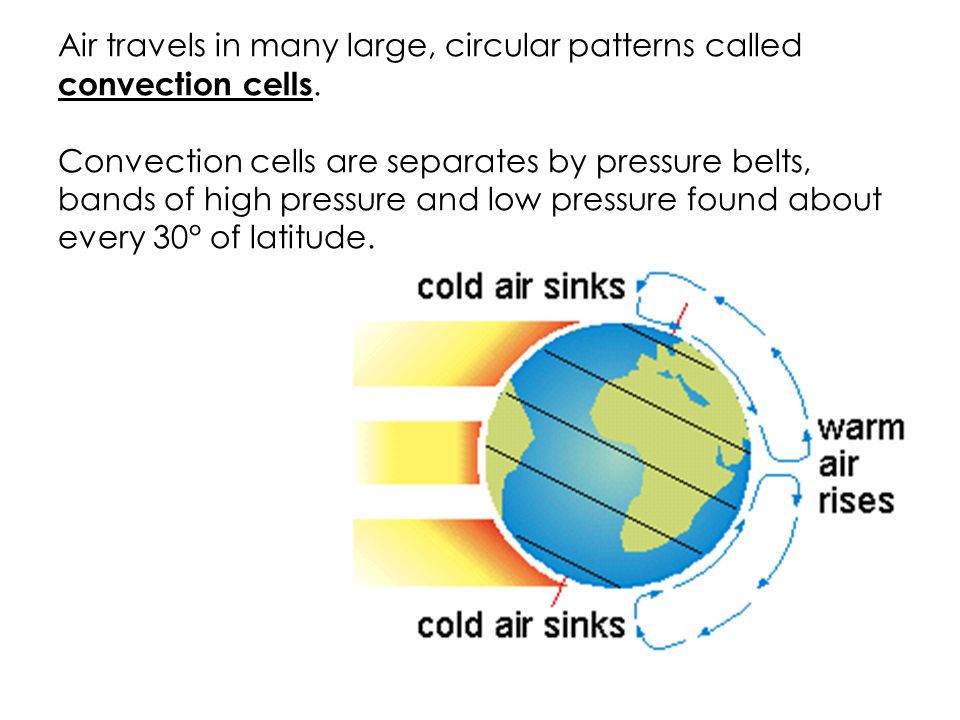
The movement of air caused by differences in air pressures is called solar energy Air is warmer and less dense than surrounding air at the equator because the equator receives more. Air travels in large CIRCULAR patterns called. Rising warm air and sinking cool air for a circular wind pattern called a.
However it is not this simple. These global wind patterns drive large bodies of air called air masses. Cool air that moves down mountain slopes during the night is called.
Warm air that rises up mountain slopes during the day is called. Flight Begins with Air in Motion As an airplane moves through the air its wings cause changes in the speed and pressure of the air moving past them. Circular movement of warm air rising and cool air sinking.
Air from the surrounding area is sucked into the space left by the rising air. The large Ls on a surface map represent centers of low pressure also known as _____ storms. The direction of this motion is ____ in the Atlantic and ____ in the Pacific.
Cool air that flows over the land toward the ocean during the night is called. The ocean gyres move clockwise in the Northern. A convection cell is most notable in the formation of clouds with its release and transportation of energy.
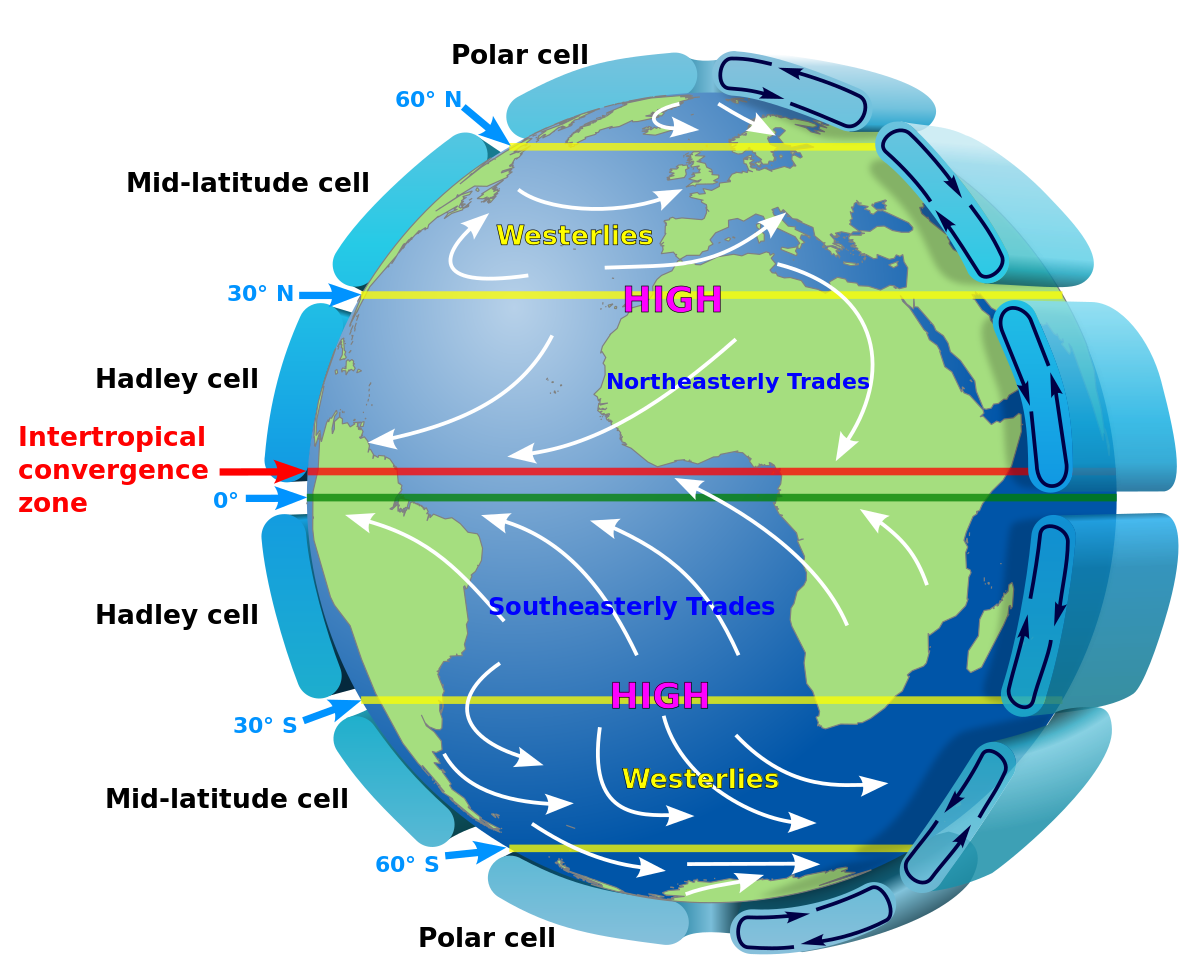
The Pacific and Atlantic Oceans have a circular pattern of surface currents called gyres that circle clockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and counterclockwise in the. Which raises the air temperatures over land between 3 to 6oC 5 to 11oF. Shady Attia in Net Zero Energy Buildings NZEB 2018.
At the poles the cooler air sinks and moves back toward the equator. The movement of air is mainly caused by the differences in pressure and temperature. This dual movement creates large circular patterns or gyres in each of the planets oceans.
Some of the examples of convection current may include boiling water convection currents in the atmosphere and in the ocean weather changes campfires etc. Horizontal flow is called advection. Transfer of energy as electromagnetic waves.
Air in the troposphere is warmer near the ground. This is the lowest layer of the atmosphere. Air movement takes place in the troposphere.
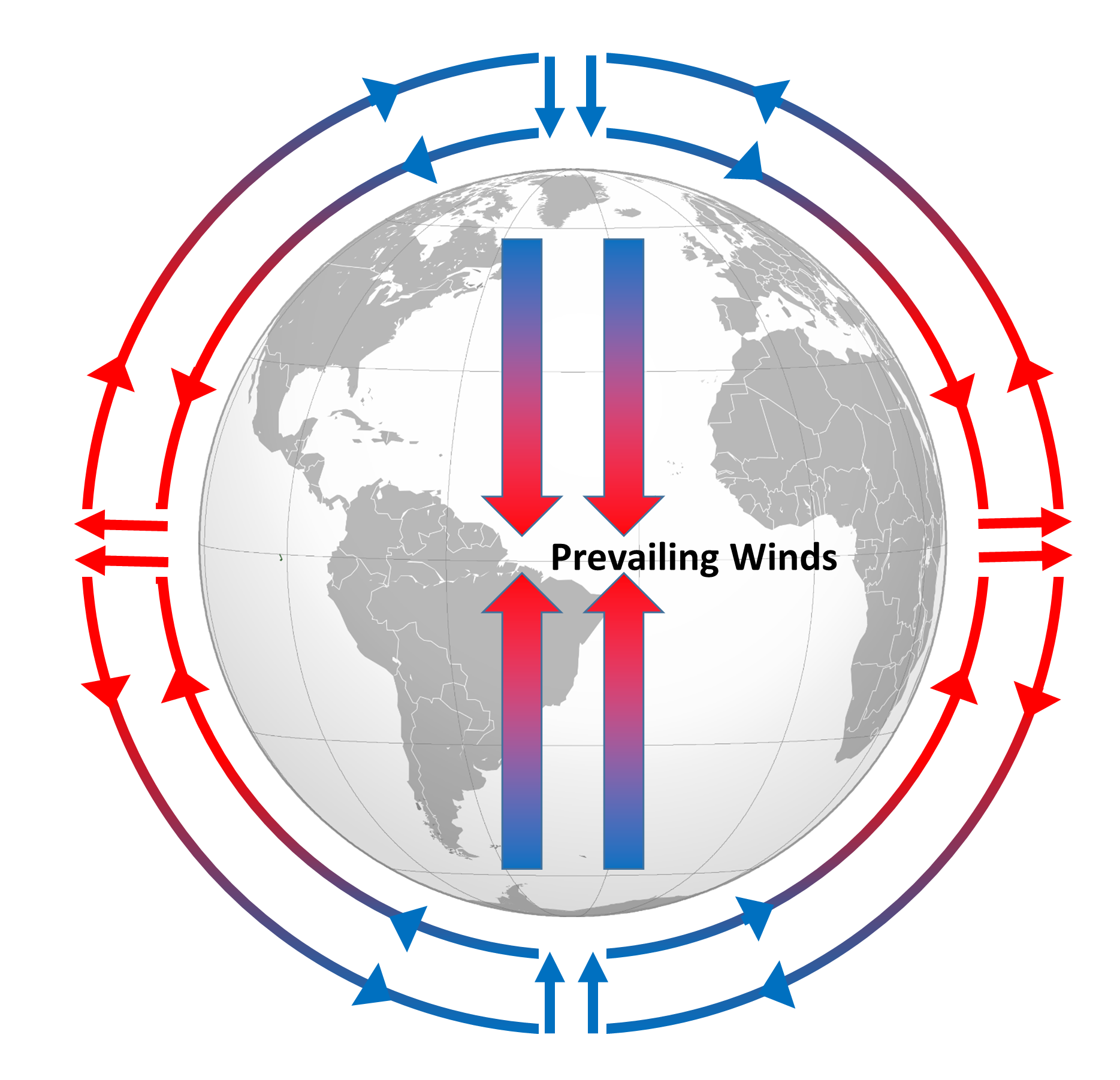
Warm air rises at the equator and moves toward the poles. This phenomenon creates wind. Movement of Air.
Water vapor carbon dioxide and other gases absorb and reradiate thermal energy. Rising air is an --------- while sinking air is a --------. To understand lift you first have to understand how air.
Air masses are thousands of feet thick and extend across large areas of the Earth. Convection cells are seperated by. Figure below shows how this happens.
The gyre then becomes the North Atlantic Current which flows across the North Atlantic to Europe. Air movement is an energy-efficient alterative to air cooling in NZEB Garde and Donn 2014Air speeds greater than 020 ms may be used to increase the upper operative temperature limits of the comfort zone under certain circumstancesThis could be achieved by using ceiling desk or pedestal fans to elevate air. What are the large circular patterns air travels in called.
Ocean currents in the Atlantic and the Pacific move in a generally circular pattern. Warm air is lighter and it rises upwards meanwhile cold air is denser and hence it moves down to replace the warm air. Convection cells form because of unequal ------- and -------- of the air.
The location over which an air mass forms will determine its characteristics. Where it reaches the ground it creates a high pressure zone. As air aloft moves from south to north air leaves the southern area and piles up.
Air flowing from areas of high pressure to low pressure creates winds. Gyres flow clockwise in Northern Hemisphere oceans and counterclockwise in Southern. These changes result in the upward force called lift.
As the prevailing winds in earths atmosphere blow across the surface of the oceans the winds push water in the direction that theyre blowing. Bands of high pressure and low pressure founf every 30degrees of latitude. As a result the surface water of the oceans moves in concert with the air above it.
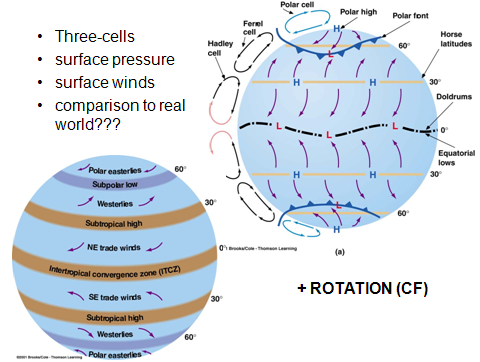
Atmospheric circulation is the large-scale movement of air through the atmosphere categorized into the Hadley Ferrel and Polar circulation cells. These differences create convection currents and winds. For example air over the tropical ocean becomes exceptionally hot and humid.
Convection currents are defined as the vertical movement of heat or moisture energy from one location to another primarily due to the temperature changes within the substance. The Gulf Stream is the western boundary current of the gyre. Air flows horizontally at top of the troposphere.
Air moves because of differences in heating. Land warms up -------. SINKING air causes HIGH PRESSure because.
In area near the equator the sun is almost directly overhead for most of the year. Transfer of energy by circulation or movement of a gas.
8 2 Winds And The Coriolis Effect Introduction To Oceanography
Ppt Chapter 1 Sections 3 4 Review Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 2325529
Global Winds And Local Winds Ppt Video Online Download

Science Notes Chapter 2 Ppt Download

A Global Look At Moving Air Atmospheric Circulation Center For Science Education

0 comments
Post a Comment